(General Science) Chemistry - Acids and Bases, Indicators, pH Scale & Changes
GENERAL SCIENCE: CHEMISTRY
ACID, BASES AND SALTS
INDICATORS
An indicator is a dye which gives different colours in acid and base. Three common indicators used to test acids and bases are Litmus, Methyl Orange, and Phenolphthalein. Litmus can be used in the form of litmus solution or in the form of litmus paper. It is of two types- blue litmus and red litmus. An acid turns blue litmus red and a base turns red litmus blue. (A water soluble base is called an alkali.)
Litmus is a natural indicator. The neutral colour of litmus is purple. Methyl orange and phenolphthalein are synthetic indicators. The neutral colour of methyl orange is orange, whereas that of phenolphthalein is colourless. Methyl orange gives red colour in an acid solution and yellow colour in a basic solution. Phenolphthalein remains colourlelss in an acid solution and gives pink colour in a basic solution.
Turmeric is also a natural indicator, and contains a yellow dye. It turns red in presence of a base. That is why yellow stains of turmeric on a cloth turn reddish-brown in contact with soap, which is basic in nature. Extract of red cabbage is a natural indicator, and is red in colour. It remains red in acidic solutions but turns green in the presence of a base.
Substances which change their smell (odour) in acidic and basic medium are called olfactory indicators. Examples: Onion and vanilla extracts. The smell of onion cannot be detected when a base is added to onion extract. However, acids do not destroy the smell of onions. Similarly, the pleasant smell of vanilla is destroyed in presence of a base but not in presence of an acid.
THE pH SCALE
The concentrations of H+ and OH- ions are equal in pure water. Acidic solutions have excess of H+ ions, whereas basic solutions have excess of OH- ions. The strengths of acid solutions and basic solutions can be represented by means of a scale, known as the pH scale, which was devised by Sorenson. This is done by making use of H+ ion concentrations in these solutions. The pH of a solution is inversely proportional to the concentration of H+ ions in it. A solution with high concentration of H+ ions has a low pH value, and vice versa. The letter 'p' in the term 'pH' stands for the German word 'potenz' (which means power) and 'H' stands for H+ ion concentration. The pH scale has values from 0 to 14.pH value is a number and has no units.
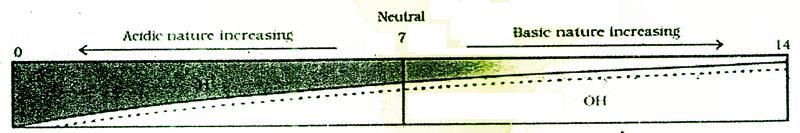
Neutral substances have a pH of exactly 7. For example, pure water, salt solution and sugar solution have a pH value of 7, i.e., they are neutral. Acids have a pH value less than 7. The lower the pH value, the stronger is the acid. Bases have a pH of more than 7. The higher the pH value, the stronger is the base. pH value of some common substances is shown in the table below.
A universal indicator is used to obtain an idea about how acidic or basic a substance is. It is a mixture of different indicators which give different colours at different pH values of the entire range on the pH scale. The universal indicator gives green colour with a neutral solution, yellow, orange or red with an acidic solution, and blue, purple or violet with a basic solution, the exact colour depending on the pH of the solution.
Importance of pH Changes
- Plant growth is best when the soil has a pH value close to 7. If the soil is too acidic then materials like quicklime, slaked lime or chalk can be added to reduce its acidity.
pH Value of Some Common Substances
| pH Value |
Example |
pH Value |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | battery acid | 8 | sea water, eggs |
| 1 | sulfuric acid | 9 | baking soda |
| 2 | lemon juice, vinegar | 10 | Great Salt Lake, milk of magnesia |
| 3 | orange juice, soda | 11 | ammonia solution |
| 4 | tomato juice, acid rain | 12 | soapy water |
| 5 | black coffee, bananas | 13 | bleach, oven cleaner |
| 6 | urine, milk | 14 | liquid drain cleaner |
| 7 | pure water | 7 |
-- |
Basicity of the soil can be reduced by adding decaying organic matter (manure or compost) which contains acidic materials.
- When the pH of rain water is about 5.6, it is called acid rain. Too much acid rain can lower the pH of water in lakes and rivers. This can make the survival of aquatic animals difficult. Calcium carbonate can be added to reduce the acidity of water in lakes and rivers.
- Life does not exist on planet Venus because it is covered with thick white and yellowish clouds of sulphuric acid.
- When a honey-bee stings a person, it injects an acidic substance into the skin which causes immense pain and irritation. Rubbing a mild base, like baking soda solution, on the affected area gives relief. When a wasp stings, it injects an alkaline liquid into the skin. Therefore, rubbing a mild acid, like vinegar, on that area gives relief. An ant's sting injects methanoic acid into the skin, which can be neutralised by rubbing baking soda solution. Some plants also give painful stings. The stinging hair of nettle plant leaves inject methanoic acid into the skin which causes burning pain. It can be relieved with the help of baking soda, or by rubbing the leaf of a 'dock' plant (which contains some basic chemical).
- The bacteria present in our mouth break down the sugar to form acids. Tooth decay starts when the pH of acid formed in the mouth falls below 5.5. Using the toothpaste, which are basic, for cleaning the teeth can neutralise the excess acid in the mouth and prevent tooth decay.
data-matched-content-ui-type="image_card_stacked"
Useful Tips & Articles
तैयारी कैसे करें? |
EXAM SUBJECTS |
STUDY RESOURCESDownload Free eBooks |



